Indonesia
Reducing industrial energy emissions in Southeast Asia’s largest economy
Indonesia is already the largest energy user in Southeast Asia, consuming nearly as much energy as Thailand, Malaysia and Singapore combined. By 2025, the Indonesian government predicts that its thriving industrial sector will account for almost half of the country’s final energy demand, and a significant amount of greenhouse gas emissions as a result. Through the implementation of energy efficient policies and management systems, Indonesia’s industrial sector could potentially conserve as much as 30 per cent of its energy use.
Why is industrial energy efficiency important for Indonesia?
Thanks to its booming economy, Indonesia has managed to halve its poverty rate in just two decades. In a country of 260 million people, energy efficiency will help to ensure long-term energy security and ongoing job creation.
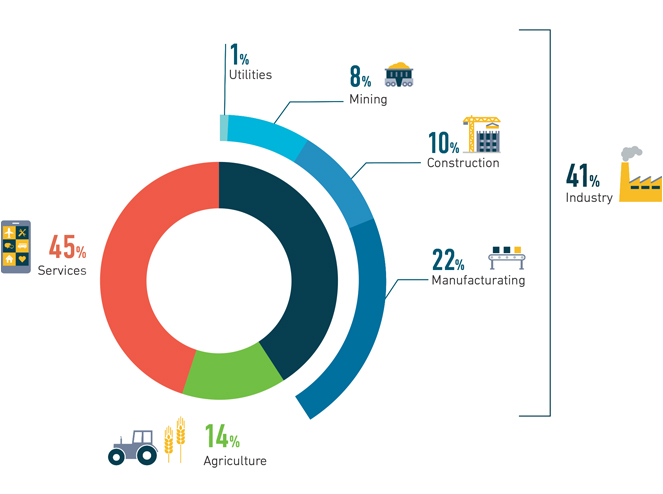
Industry drives economic growth in Indonesia, contributing 41 per cent to total GDP in 2016. Over the last 12 years, mining has contributed the industrial sector’s largest share to GDP, followed by food and tobacco. Industrial energy efficiency could catalyse a new market for energy services and give Indonesia a competitive advantage as its economy continues to grow.
In a business as usual scenario, Indonesia’s energy use threatens to become its highest contributor to greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions, overtaking the emissions generated from deforestation and land use. Industrial energy efficiency would help to limit emissions and mitigate climate change as the economy continues to grow.
Accelerating industrial energy efficiency in Indonesia
Industry will play an important role in reducing GHG emissions as the Indonesian economy continues to grow. The country already boasts the second largest market for energy efficiency implementation in the ASEAN region. However, electricity subsidies and limited low-interest financing schemes mean there has been very little incentive for industry to reduce its energy bills or invest in efficient technology and management systems. This is particularly the case for small to medium sized enterprises with fewer resources to invest in energy efficiency improvements.
Key service areas
Financing solutions
After examining the ecosystem of existing industrial energy efficiency initiatives in Indonesia — many of which focus on policy reform and general awareness raising — the Accelerator identified a gap within the financial services sector.
The Accelerator’s design of a national seed-fund to provide concessional debt for industrial energy efficiency projects will allow for large-scale proof of concept demonstrations in key industries such as mining, textiles and cement production.
Simultaneously, the design and introduction of de-risking instruments such as energy savings insurance aims to attract more private sector capital to the national energy efficiency market.